Concept 35 DNA responds to signals from outside the cell.
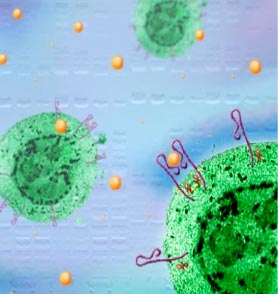
Growth and development require that cells communicate with each other and react to signals that come from other parts of the body. Notably, hormones released by various glands travel throughout the body to stimulate the growth of certain cell types. Cells capable of being stimulated by a particular hormone possess a specific receptor anchored in the cell membrane. The binding of a hormone to its receptor initiates a series of molecular transformations, called signal transduction, that relay the growth signal through the cell.
First, the receptor transduces the signal through the cell membrane to the internal membrane surface, where it activates protein "messengers." These messengers are part of and initiate a cascade of chemical reactions, often involving the addition of phosphate groups. This is the signal that passes through the cytoplasm and into the nucleus. In the final step of signal transduction, DNA binding proteins attach to regulatory sequences and start DNA replication or transcription.
 DNA is packaged in a chromosome.
DNA is packaged in a chromosome. Higher cells incorporate an ancient chromosome.
Higher cells incorporate an ancient chromosome. Some DNA does not encode protein.
Some DNA does not encode protein. Some DNA can jump.
Some DNA can jump. Genes can be turned on and off.
Genes can be turned on and off. Genes can be moved between species.
Genes can be moved between species. DNA responds to signals from outside the cell.
DNA responds to signals from outside the cell. Different genes are active in different kinds of cells.
Different genes are active in different kinds of cells. Master genes control basic body plans.
Master genes control basic body plans. Development balances cell growth and death.
Development balances cell growth and death. A genome is an entire set of genes.
A genome is an entire set of genes. Living things share common genes.
Living things share common genes. DNA is only the beginning for understanding the human genome.
DNA is only the beginning for understanding the human genome.